
It embodies the discipline of rigorous financial planning and sensitivity analysis, pushing us to think in probabilities rather than possibilities. To calculate the PI, we need the estimated future cash flows to be generated from a project and the WACC for it. Profitability index is a profit investment ratio that helps evaluate what is cost of goods sold and how do you calculate it the potential profitability of an investment. The profitability index considers the time value of money, allows companies to compare projects with different lifespans, and helps companies with capital constraints choose investments. The factory expansion project has a higher profitability index and a more attractive investment.
What are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Profitability Index in Excel?
If the PI is less than 1, it means you will not even recover your initial investment. It helps you forecast the returns and feasibility of a project to see if it is even worthwhile to invest. Profitability index is a technique to evaluate the viability of investments/projects. But the company also needs to consider other projects where the PI may be more than 1.3.
Formula of profitability index (PI)
This involves projecting the cash that an investment will generate and then discounting it to its present value. This discounting accounts for the time value of money – a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. Imagine a compass that guides investors through the intricate landscape of potential profitability. The profitability index serves as that compass, offering a numerical measure of a project’s profitability based on its future discounted returns in relation to the initial investment.
Effectiveness of PI
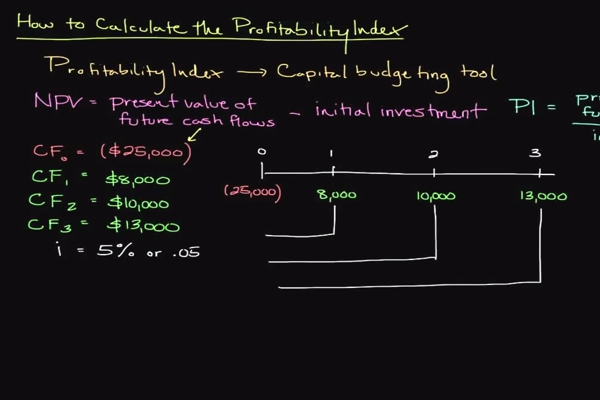
- To calculate NPV all, we need to do is to add up all discounted cash flows and then deduct the initial investment required.
- Suppose further that the company has only $40,000 available to invest and all the projects are independent, not mutually exclusive.
- The index itself is a calculation of the potential profit of the proposed project.
- Now that we have obtained the PI value for both the projects, let’s look into its application for appraising projects.
- Its user-friendly interface ensures that users, regardless of their level of financial expertise, can effortlessly input the necessary data and obtain accurate results.
- A project with a high PI but small scale might contribute less overall value than a larger project with a lower PI.
The profitability index (PI) helps measure the attractiveness of a project or investment. It is calculated by dividing the present value of future expected cash flows by the initial investment amount in the project. A PI greater than 1.0 is considered a good investment, with higher values corresponding to more attractive projects. For example, a project with an initial investment of $1 million and a present value of future cash flows of $1.2 million would have a profitability index of 1.2. Based on the profitability index rule, the project would proceed, even though the initial capital expenditure required are not identified.
Also, it helps comparison by evaluating all big and small investments in terms of per unit of investment. Step 5) Divide the present value of cash flows by the initial investment. When applying the PI technique to check on the profits expected from a project, it is recommended to not consider the size of the project. It is because there are instances where there re larger cash flows, but then the PI is limited due to the restricted profit margins. Hence, it is important to be wise when implementing this technique for accurate results.
Different industries have varying risk profiles and investment scales, influencing how PI is used in investment appraisal. Ascertain whether an investment is viable with computed input of ROI to allow an informed decision on investment management. We can see that the PI number obtained through our incremental analysis is greater than 1.
PI is particularly beneficial in capital budgeting to evaluate the desirability of investments or projects with constrained funding. The strategic benefits of using the Profitability Index for financial decision-making are nothing short of transformative. This metric empowers us to perform a deep financial analysis that goes beyond mere gut feelings or intuition. We can realistically forecast the value each investment brings to the table and prioritize capital allocation accordingly.
If we compare both of these formulas, they both will give the same result. However, both PIs are less than 1.0, so the company may forgo either project. Since the PI is greater than 1, then you should consider to invest in the project. Since the Profitability Index is greater than 1, then you should consider to invest in the project. There are different ways to calculate PI, and they include Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period.
This straightforward formula belies the powerful insight it offers – a direct measure of the investment’s efficiency. As you can see, Bob’s investment has a PI ratio of 2, which indicates that it is highly profitable. On the other hand, Tim’s investment has a PI ratio of 0.4, which means that it is not profitable. The PI ratio will result in a number that is 1, less than 1 or bigger than 1. Generally the PI ratio of 1 is least acceptable as it represents the break even point of a project, which defines the point where total sales (revenue) equal to the total cost. A PI ratio of less than 1 is completely undesirable as it represents that a project will cost more than it is expected to earn.
