The first step in calculating efficiency variance is to determine the budgeted quantity. This is the expected output established at the beginning of the measuring period. It may be based on historical data, industry benchmarks, or other factors specific to the company’s operations. The budgeted quantity should be a realistic estimate of what can be achieved under normal operating conditions. Efficiency variance is essential in the manufacturing industry because it can impact a company’s profitability and competitiveness.
Standard Costing Outline
This can occur when quality standards are not correctly defined or lack monitoring and enforcement. Inadequate training of employees can lead to mistakes, rework, and reduced efficiency. This can occur accounting for derivatives definition, example when employees are not properly trained on the operation of equipment, safety procedures, or quality control standards. Inefficient material handling can lead to increased costs and reduced efficiency.
Lack of Resources – Potential Roadblocks A Company May Encounter When Addressing Efficiency Variance

This involves looking beyond the numbers to understand the underlying factors contributing to the variances. For example, if a material price variance is detected, managers should examine market conditions, supplier performance, and procurement strategies to pinpoint the cause. Similarly, if a material quantity variance is found, a thorough review of the production process, employee performance, and equipment efficiency is necessary. This investigative approach ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective.
Employee Training – Best Practices for Addressing Efficiency Variance
- In the NoTuggins example, the total standard direct materials allowed was 630,000 feet.
- All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
- Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency analysis and implementing improvements.
- In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is \(0.20\) pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the standard quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds.
In addition to improving profitability and efficiency, monitoring efficiency variance can help companies stay competitive. By optimizing their operations and reducing costs, companies can offer their products or services at more competitive prices, which can help them to attract and retain customers. Moreover, we will discuss the role of technology in reducing efficiency variance, common causes of efficiency variance, and best practices for addressing it in a manufacturing plant. Additionally, we will explore when a company should consider investing in new equipment, outsourcing specific processes, and how to ensure that employees are properly trained to minimize efficiency variance.
During the period, Brad projected he should pay $675,000 for direct labor to produce 150,000 units. The standard and actual amounts for direct labor hours, rates, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct labor variance template. Once the top section is complete, the amounts from the top section can be plugged into the formulas to compute the direct labor efficiency (quantity) and rate (price) variances.
Industry Standards – When Should a Company Consider Investing in New Equipment
” If it was caused by errors and/or inefficiencies, it cannot be assigned to the inventory. Errors and inefficiencies are never considered to be assets; therefore, the entire amount must be expensed immediately. Standard costs are sometimes referred to as the “should be costs.” DenimWorks should be using 278 yards of denim to make 100 large aprons and 60 small aprons as shown in the following table. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
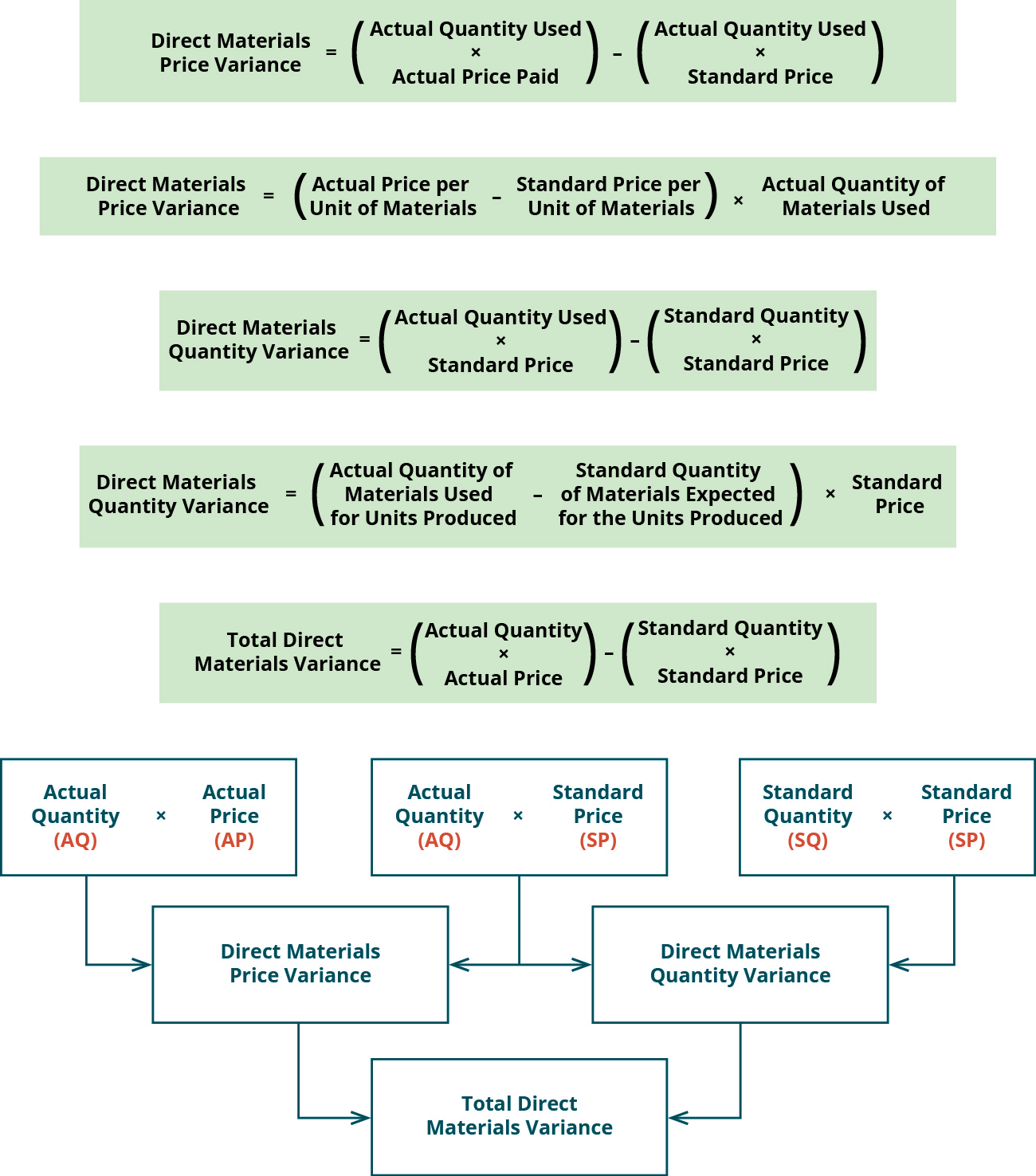
If the manufacturer uses more direct materials than the standard quantity of materials for the products actually manufactured, the company will have an unfavorable direct materials usage variance. Figure 10.35 shows the connection between the direct materials price variance and direct materials quantity variance to total direct materials cost variance. It is one of the two components (the other is direct material price variance) of direct material total variance.
Total variable manufacturing overhead costs per the standard amounts allowed are calculated as the total standard quantity of 37,500 times the standard rate per hour of $3 equals $112,500. During the period, Brad projected he should pay $112,500 for variable manufacturing overhead to produce 150,000 units. Refer to the total direct materials variance in the top section of the template. Total standard quantity is calculated as standard quantity per unit times actual production or 4.2 feet of flat nylon cord per unit times 150,000 units produced equals 630,000 feet of flat nylon cord.
These tools can also integrate with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, ensuring that data is accurate and up-to-date. Efficiency variance can be categorized into different types based on the resources being analyzed. These categories help businesses focus on specific areas where improvements can be made.
