The template provided in Exhibit 8-3 can be used to compute the total direct material variance, direct material quantity variance, and direct material price variance. Once the top section is complete, the amounts from the top section can be plugged into the formulas to compute the variable manufacturing overhead efficiency (quantity) and rate (price) variances. The goal is to determine how much should have been incurred to produce the actual quantity of units produced and compare that to how much was actually incurred to produce the actual quantity of units produced. As mentioned previously, standard rates and quantities are established for variable manufacturing overhead.
Practice Video Problem 8-1: Computing direct materials variances LO2
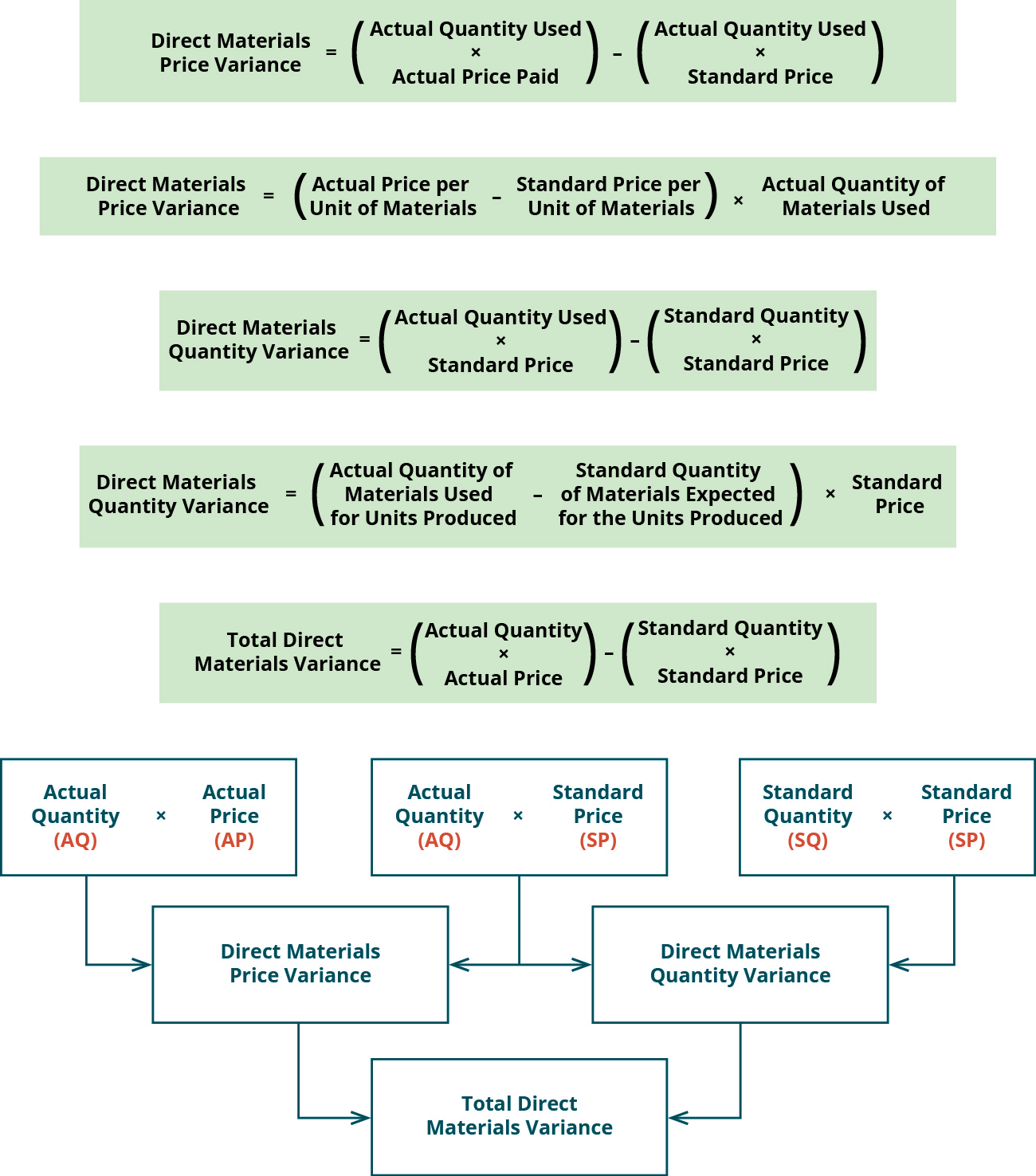
The first step in this analysis is to regularly review variance reports, which provide a snapshot of how actual costs compare to standard costs. These reports should be detailed and timely, allowing managers to quickly identify and address any discrepancies. Direct material price variance (DM Price Variance) is defined as the difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials. It evaluates the extent to which the standard price has been over or under applied to different units of purchase.

Video Illustration 8-3: Computing direct labor variances
By analyzing historical data, businesses can identify key drivers of variances and quantify their impact. For example, regression analysis might reveal that a 10% increase in supplier lead time results in a 5% increase in material quantity variance. Armed with this knowledge, companies can focus their efforts on improving supplier lead times to achieve better cost control. Additionally, the use of variance tax forms and what you need them for decomposition allows businesses to break down complex variances into more manageable components, providing deeper insights into specific areas of concern. Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver quality materials at agreed-upon prices help maintain stable production costs. Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances.
Types of Efficiency Variances
Conversely, when a company is less efficient than expected, it may experience decreased revenue and increased costs, negatively impacting its profitability. The third step is to find the actual output achieved during the measuring period. This is the quantity of units produced or services rendered, as measured by the company’s production system or other tracking methods. The actual amount should be a reliable and accurate reflection of what was achieved during the measuring period.
- Implementing a robust quality control program can help to reduce efficiency variance.
- If you want to improve your manufacturing process’s efficiency and profitability, this guide is for you.
- A culture that promotes continuous improvement and values employee input can lead to innovative solutions that enhance efficiency.
- This involves conducting root cause analysis to uncover the factors contributing to inefficiencies.
The most common causes of labor variances are changes in employee skills, supervision, production methods capabilities and tools. Therefore, always consult with accounting and tax professionals for assistance with your specific circumstances. Explore methods to calculate efficiency variance, understand its impact, and discover strategies and technologies to enhance operational efficiency.
How Poor Data & Analytics Access Hinders Manufacturing Cost Understanding – And What To Do About It
However, they were able to produce the 150,000 units using less material, which is favorable. If the actual amount exceeds the standard amount, the variance is unfavorable (U) indicating they used or paid more than the standard amount, which is unfavorable. The standard price of materials purchased by Angro is $2.00 per kg and standard quantity of materials allowed to produce a unit of product is 1.5kg.
Ignoring efficiency variance can lead to a lost competitive edge, as competitors who address efficiency variance can better produce high-quality products at a lower cost. Efficiency variance can increase costs, such as higher labor costs, materials waste, and increased energy consumption. Ignoring efficiency variance can lead to continued waste and inefficiencies, resulting in increased costs for the company. The operations manager works closely with the production manager to ensure that production processes are optimized and that efficiency variance is minimized. They also work with other departments, such as finance and marketing, to ensure that operations are aligned with the company’s overall goals.
By analyzing this variance, businesses can identify areas where overhead costs can be controlled or reduced, leading to more efficient operations. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for direct materials, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. The direct material standards for one unit of NoTuggins are 4.2 feet of flat nylon cord that costs $0.50 per foot for a total direct material cost per unit of $2.10. During the period, 600,000 feet of flat nylon cord costing $330,000 were purchased and used. Premium Furniture, a US based Inc., uses a standard costing system to control its direct materials and conversion costs.
The operations manager is responsible for overseeing the overall operations of the company. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the remainder of our explanation, we will use a common format for calculating variances. The amounts for each column are computed in the order indicated in the headings. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
